High alert Medications & Look alike Sound alike Drugs
Table of Contents
High-Alert/Risk Medications
High-alert medications are drugs that have a high risk of causing significant harm to patients if used incorrectly. These medications require extra precautions, such as independent double checks, tall man lettering, and special labeling/storage.
Examples of High-Alert Medications (Based on ISMP List):
Examples of High-Alert Medications (Based on ISMP List):
- Anticoagulants – Warfarin, Heparin, Enoxaparin
- Insulins – Insulin Aspart, Insulin Glargine
- Opioids – Morphine, Hydromorphone, Fentanyl
- Chemotherapy Agents – Methotrexate, Vincristine
- Neuromuscular Blockers – Succinylcholine, Rocuronium
- Potassium Concentrates – Potassium Chloride injection
- Hypertonic Saline (greater than 0.9%)
What are Look Alike Sound Alike Drugs (LASA)
Look Alike Sound Alike medications are drugs that look or sound similar to other medications, increasing the risk of medication errors. The ISMP (Institute for Safe Medication Practices) and FDA recommend strategies like Tall Man Lettering, separate storage, and barcode scanning to minimize errors.Look Alike Sound Alike Drugs – Error Prevention Strategies
1. Tall Man Lettering
- Use uppercase letters to highlight differences in similar drug names.
- Example: hydrOXYzine vs. hydrALAZINE, clonazePAM vs. clonidine
- Helps distinguish visually similar names in prescribing and labeling.
2. Separate Storage and Labeling
- Store LASA medications in different sections of the pharmacy.
- Use warning labels or colored bins for differentiation.
- Example: Keeping Lantus (insulin glargine) away from Latuda (lurasidone).
3. Barcode Scanning
- Ensures the correct medication is dispensed and administered.
- Reduces human error in verifying drug name and strength.
4. Verbal Confirmation and Read-Back
- When taking verbal orders, repeat back the drug name, strength, and dosage.
- Use phonetically clear communication (e.g., “D as in Delta” for clarity).
5. Indication-Based Prescribing
- Include the drug’s indication on prescriptions to differentiate similar-sounding names.
- Example: Metformin (for diabetes) vs. Metronidazole (for infection).
6. Limiting Abbreviations
- Avoid dangerous look-alike abbreviations (e.g., “MgSO₄” for magnesium sulfate vs. morphine sulfate).
- Write the full drug name clearly.
7. Patient Counseling
- Encourage patients to verify their medications before leaving the pharmacy.
- Teach patients to check pill shape, color, and imprint codes.
8. Use of Alerts in Pharmacy Software
- Implement computerized alerts for high-risk LASA medications.
- Example: A pop-up warning for Celebrex (celecoxib) vs. Celexa (citalopram).
9. Independent Double-Checks
- Require a second pharmacist or technician to verify the medication before dispensing.
- Particularly important for high-alert drugs like insulin, opioids, and anticoagulants.
10. Staff Education & Awareness
- Regular LASA training for pharmacy staff.
- Maintain an updated LASA list in the pharmacy for quick reference.
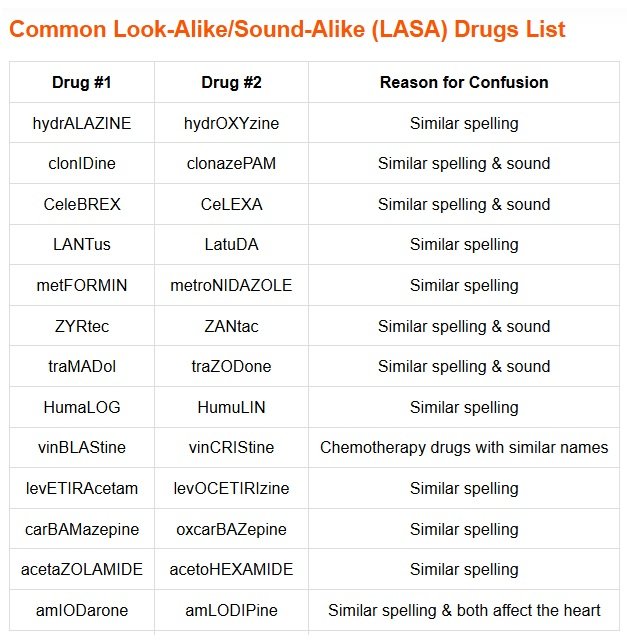
Common Look-Alike/Sound-Alike (LASA) Drugs List
| Drug #1 | Drug #2 | Reason for Confusion |
| hydrALAZINE | hydrOXYzine | Similar spelling |
| clonIDine | clonazePAM | Similar spelling & sound |
| CeleBREX | CeLEXA | Similar spelling & sound |
| LANTus | LatuDA | Similar spelling |
| metFORMIN | metroNIDAZOLE | Similar spelling |
| ZYRtec | ZANtac | Similar spelling & sound |
| traMADol | traZODone | Similar spelling & sound |
| HumaLOG | HumuLIN | Similar spelling |
| vinBLAStine | vinCRIStine | Chemotherapy drugs with similar names |
| levETIRAcetam | levOCETIRIzine | Similar spelling |
| carBAMazepine | oxcarBAZepine | Similar spelling |
| acetaZOLAMIDE | acetoHEXAMIDE | Similar spelling |
| amIODarone | amLODIPine | Similar spelling & both affect the heart |
| oxyCODONE | HYDROcodone | Similar drug class & name |
| morphine | HYDROmorphone | Both are opioids |
| ALPRAZolam | LORazepam | Both are benzodiazepines |
| predniSONE | prednisoLONE | Both corticosteroids |
| buPROPion | busPIRone | Similar spelling & sound |
| riSPERidone | ropINIRole | Similar spelling & sound |
Look-Alike Sound-Alike Packaging Issues
Look-alike sound-alike (LASA) packaging issues occur when products have similar appearances (colors, shapes, logos) or names (phonetically or spelling-wise). This leads to confusion, misuse, or even dangerous errors in Pharmacy setting.
Look-Alike Packaging:
- Similar pill colors, shapes, or bottle designs (e.g., Zantac vs. Xanax, Lamictal vs. Lamisil).
- IV bags or injectables with nearly identical labels.
Over-the-Counter (OTC) Drugs & Supplements
- Store-brand vs. name-brand similarities (e.g., Tylenol® vs. generic acetaminophen).
- Sleep aids, pain relievers, or allergy meds with nearly identical packaging.
- Sound-alike supplements (e.g., Serenalin vs. Sertraline, mimicking an antidepressant).
Frequently asked Questions
What are Look-Alike/Sound-Alike (LASA) drugs?
Answer: LASA drugs are medications with similar names in spelling or pronunciation, increasing the risk of medication errors. These errors can occur during prescribing, dispensing, or administration, leading to potential patient harm.How can pharmacists and pharmacy technicians prevent LASA medication errors?
Answer: Strategies to prevent LASA medication errors include:- Tall Man Lettering (e.g., predniSONE vs. prednisoLONE)
- Barcode scanning before dispensing medications
- Verbal confirmation and read-back when taking verbal orders
- Storing LASA medications separately to avoid mix-ups
- Including medication indications on prescriptions
Why is Tall Man Lettering used for LASA drugs?
Answer: Tall Man Lettering highlights differences in similar drug names by using uppercase letters, making it easier to distinguish between look-alike medications.For example, vinBLAStine vs. vinCRIStine helps prevent fatal chemotherapy mix-ups.
What role does the FDA and ISMP play in reducing LASA medication errors?
Answer: The FDA (Food and Drug Administration) and ISMP (Institute for Safe Medication Practices) identify and publish lists of LASA drugs, promote best practices like Tall Man Lettering, and recommend the use of electronic prescribing, barcode scanning, and pharmacist verification to reduce medication errors.Which organization publishes a list of look alike sound alike medications?
The Institute for Safe Medication Practices (ISMP) and the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) are the primary organizations that publish and maintain lists of look-alike/sound-alike (LASA) medications to help prevent medication errors.1. ISMP’s List of Confused Drug Names
Website: www.ismp.org (FDA and ISMP Lists of Look-Alike Drug Names with Recommended Tall Man Letters)What’s Included:
- Regularly updated list of drug pairs with similar names or packaging.
- Recommendations for preventing mix-ups (e.g., Tall Man Lettering).
- Clonidine (blood pressure) vs. Klonopin (anxiety)
- Zyrtec (allergy) vs. Zyprexa (antipsychotic)
2. FDA’s LASA Medication Lists
Website: www.fda.govWhat’s Included:
- Drug name screening during approval process.
- Public alerts on confusing drug names.
- MedWatch Program for reporting errors.
What is the difference between look alike and sound alike drugs
Both look-alike and sound-alike (LASA) drugs pose risks for medication errors, but they differ in how they cause confusion:| Factor | Look-Alike Drugs |
Sound-Alike Drugs
|
| Primary Cause | Similar packaging, labeling, or appearance (e.g., pill shape/color, bottle design). |
Similar names when spoken or written (phonetic or spelling similarities).
|
| Examples |
|
|
| Risk Scenario | A nurse grabs the wrong box due to nearly identical labels. |
A pharmacist misheard a drug name during a verbal order.
|
| Prevention Strategies |
|
|
| Regulatory Focus | FDA reviews drug labeling & packaging to minimize visual mix-ups. |
FDA screens drug names before approval to avoid sound-alike confusion.
|